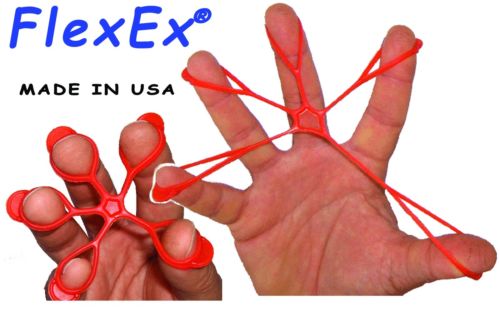
FlexEx can be useful in combating and treating many of the following hand and wrist injuries.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is pressure on the median nerve – the nerve in the wrist that supplies feeling and movement to parts of the hand. It can lead to numbness, tingling, weakness, or muscle damage in the hand and fingers.
The median nerve provides feeling and movement to the “thumb side” of the hand (the palm, thumb, index finger, middle finger, and thumb side of the ring finger). The area in your wrist where the nerve enters the hand is called the carpal tunnel. This tunnel is normally narrow, so any swelling can pinch the nerve and cause pain, numbness, tingling or weakness. This is called carpal tunnel syndrome, and can be relieved and rehabilitated using the FlexEx.
May 6, 2013
Who is most like to get carpal tunnel syndrome?
People most at risk are those with jobs or activities that involve repetitive finger use, especially those associated with high force, long-term use, extreme wrist motions, and vibration.
Symptoms
Symptoms usually begin slowly and can occur at any time. Early symptoms include numbness at night, tingling, and/or pain in the fingers (especially the thumb, index, and middle fingers). In fact, because some people sleep with their wrists curled, nighttime symptoms are common and can awake people from sleep. These nighttime symptoms are often the first reported symptoms. Shaking the hands helps relieve symptoms in the early stage of the condition.
DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis
Definition – Tenosynovitis implies inflammation of a tendon and its enveloping sheath; deQuervain’s tenosynovitis is a specific type of this entity which involves the tendons of two specific muscles on the thumb side of the hand – the abductor pollicis longus (APL) and the extensor pollicis brevis (EPB). These muscles are located in the forearm and their tendons travel across the wrist (through a “tunnel” termed the first dorsal compartment) on the thumb side to produce movement of the thumb. The walls of the affected tendon sheaths (basically protective coverings for the tendons) become thickened and inflamed, causing the symptoms described in the next section. The condition is 10 times more common in women, more often arises in the dominant hand, and usually occurs between the ages of 35 and 55.
Signs and Symptoms – Patients typically complain of the gradual onset of pain over the area indicated above by the red dot (over the radial styloid, an area of a bone in the forearm) when they use their thumb on the affected hand. The sufferer may relate that the pain has gradually increased over that past few weeks or months. The patient experiences difficulties with gripping and pinching, and in severe cases, the affected hand may be too painful to use. The pain may radiate into the thumb, or up into the forearm or shoulder. Examination of the affected area reveals thickening and tenderness. A test commonly used to evaluate the presence of this disease is Finkelstein’s test; the patient is instructed to grasp the thumb of the affected hand with the other fingers and actively pull the thumb towards the small finger. Sharp pain will be elicited over the area indicated by the red dot if the patient suffers from deQuervain’s tenosynovitis. This condition must be differentiated from arthritis at the base of the thumb. If the disease is allowed to progress without treatment, it is possible that fibrosis within the tendon sheath may result and a clinical picture similar to trigger finger (see other section) may result with limited motion. Ultrasound examination has recently been used to confirm the diagnosis and can be used to follow up after treatment.
Possible causes – The precise cause of deQuervain’s tenosynovitis is unknown. It is thought that excessive friction from overuse of the thumb and wrist (excessive and repetitive gripping and grasping actions) may be a factor, leading to thickening of the tissues in the compartment housing the APL and EPB tendons. For example, cases have been described in bricklayers, those who sew, piano players, fly fishermen, and golfers. It has also been hypothesized that the condition in some cases may be associated with acute injury to the involved area (direct blow to the forearm or wrist, falling on the thumb). However, most cases appear to be associated with a more monotonous, “chronic trauma” picture as mentioned above.
Treatment Options – Rest of the thumb and wrist with or without splinting to reduce the possible aggravating friction on the tendons tends to afford a slow recovery. Applying ice at the radial styloid (the bony eminence on the thumb side of the wrist where the tendons pass) may also decrease inflammation and symptoms. Initial more aggressive therapy involves injection of the first dorsal compartment (the area which houses the involved tendons) with a mixture of an anti-inflammatory drug (steroid) and local anesthetic. It may also be helpful to place the affected wrist in a removable splint to immobilize the thumb and prevent further irritation and inflammation. A recent study concluded that injecting this compartment can provide complete relief of symptoms. If symptoms improve, adding gentle stretching exercises (stretch the thumb into the palm) can prevent recurrent inflammation. If the symptoms persist after injection, then the injection can be repeated (30% of cases require reinjection after one year). If 2-3 injections over a 3-5 week period fail to give relief, then surgical management becomes appropriate.
Surgical management involves incising the skin, identifying and cutting the diseased tendon sheath under local anesthesia, and applying a compression bandage. Patients can usually return to their normal activities within 2-3 weeks after surgery. This procedure is successful 90% of the time.
Tennis Elbow
Tennis or Elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is the probably one of the most, if not the most common injury in individuals that require medical attention for elbow pain. It is not know what exactly causes tennis elbow , however, it is thought to be due to small tears of the tendons that attach forearm muscles to the arm bone at the elbow joint. Treatment of tennis elbow can often be frustrating for individuals who suffer from this ailment, but exercises with the FlexEx can help your symptoms.
February 14, 2019
Verified Purchase
What a great, simple invention. As a competitive tennis player, using the finger exercise bands relieved my annoying, debilitating tennis elbow in short order and has kept it away for a long time. Also works for golfers who like to hold the club too tightly and therefore suffer the same pain. Strongly recommend.
Learn More About Tennis Elbow Here.
Golfer's Elbow
Golfer's elbow is a condition that causes pain where the tendons of your forearm muscles attach to the bony bump on the inside of your elbow. The pain might spread into your forearm and wrist.
Golfer's elbow is similar to tennis elbow, which occurs on the outside of the elbow. It's not limited to golfers. Tennis players and others who repeatedly use their wrists or clench their fingers also can develop golfer's elbow.
The pain of golfer's elbow doesn't have to keep you off the course or away from your favorite activities. Rest and appropriate treatment can get you back into the swing of things.
Causes
Golfer's elbow, also known as medial epicondylitis, is caused by damage to the muscles and tendons that control your wrist and fingers. The damage is typically related to excess or repeated stress — especially forceful wrist and finger motions. Improper lifting, throwing or hitting, as well as too little warmup or poor conditioning, also can contribute to golfer's elbow. More
Arthritis of the Hand
The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints are affected by arthritis, activities of daily living can be difficult. Arthritis can occur in many areas of the hand and wrist and can have more than one cause.
Over time, if the arthritis is not treated, the bones that make up the joint can lose their normal shape. This causes more pain and further limits motion. However, using the FlexEx Hand Exerciser can help eliminate and relieve Hand Arthritis symptoms.
December 26, 2017
This device has been immensely helpful with alleviating arthiritic pain. There are no complicated instructions to the use of the device, which makes easy to use. I highly recommend this product for anyone suffering from arthritis, or trying to increase strength/ grip in your hand(s).
Click to learn more about Arthritis in the Hands. More
Other Useful Information & Articles:
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Days Away From Work for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Hand Rehabilitation Clinics
- Tennis Elbow
- Golfer's Elbow
- DeQuervain's Tenosynovitis
- Arthritis in the Hands
- Finger,Hand and Wrist Injuries
Email: info@FlexEx.com * Phone: 888-FlexEx9 * Phone: 888-353-9399 *